Designing data products
Working backwards from use cases
Working backwards from the end goal is a core principle of software development, and we’ve found it to be highly effective in modelling data products. In this article we'll explore a step-by-step, methodical approach to identifying data products that avoids overdesign while providing just enough clarity for teams to begin implementation. Starting with a use case, we work backward to define data products and establish their boundaries. By overlaying additional use cases, we generalise the data products to prevent overfitting. Finally, we assign domain ownership and define service level objectives to guide the architecture and implementation.
10 December 2024
One of the earliest questions organisations need to answer when adopting data mesh is: “Which data products should we build first, and how do we identify them?” Questions like “What are the boundaries of data product?”, “How big or small should it be?”, and “Which domain do they belong to?” often arise. We’ve seen many organisations get stuck in this phase, engaging in elaborate design exercises that last for months and involve endless meetings.
We’ve been practicing a methodical approach to quickly answer these important design questions, offering just enough details for wider stakeholders to align on goals and understand the expected high-level outcome, while granting data product teams the autonomy to work out the implementation details and jump into action.
What are data products?
Before we begin designing data products, let’s first establish a shared understanding of what they are and what they aren’t.
Data products are the building blocks of a data mesh, they serve analytical data, and must exhibit the eight characteristics outlined by Zhamak in her book Data Mesh: Delivering Data-Driven Value at Scale.
Discoverable
Data consumers should be able to easily explore available data products, locate the ones they need, and determine if they fit their use case.
Addressable
A data product should offer a unique, permanent address (e.g., URL, URI) that allows it to be accessed programmatically or manually.
Understandable (Self Describable)
Data consumers should be able to easily grasp the purpose and usage patterns of the data product by reviewing its documentation, which should include details such as its purpose, field-level descriptions, access methods, and, if applicable, a sample dataset.
Trustworthy
A data product should transparently communicate its service level objectives (SLOs) and adherence to them (SLIs), ensuring consumers can trust it enough to build their use cases with confidence.
Natively Accessible
A data product should cater to its different user personas through their preferred modes of access. For example, it might provide a canned report for managers, an easy SQL-based connection for data science workbenches, and an API for programmatic access by other backend services.
Interoperable (Composable)
A data product should be seamlessly composable with other data products, enabling easy linking, such as joining, filtering, and aggregation, regardless of the team or domain that created it. This requires supporting standard business keys and supporting standard access patterns.
Valuable on its own
A data product should represent a cohesive information concept within its domain and provide value independently, without needing joins with other data products to be useful.
Secure
A data product must implement robust access controls to ensure that only authorized users or systems have access, whether programmatic or manual. Encryption should be employed where appropriate, and all relevant domain-specific regulations must be strictly followed.
Simply put, it's a self-contained, deployable, and valuable way to work with data. The concept applies the proven mindset and methodologies of software product development to the data space.
Data products package structured, semi-structured or unstructured analytical data for effective consumption and data driven decision making, keeping in mind specific user groups and their consumption pattern for these analytical data
In modern software development, we decompose software systems into easily composable units, ensuring they are discoverable, maintainable, and have committed service level objectives (SLOs). 1 Similarly, a data product is the smallest valuable unit of analytical data, sourced from data streams, operational systems, or other external sources and also other data products, packaged specifically in a way to deliver meaningful business value. It includes all the necessary machinery to efficiently achieve its stated goal using automation.
1: we refer to such a unit as an architectural quantum
Data products package structured, semi-structured or unstructured analytical data for effective consumption and data driven decision making, keeping in mind specific user groups and their consumption pattern for these analytical data.
What they are not
I believe a good definition not only specifies what something is, but also clarifies what it isn’t.
Since data products are the foundational building blocks of your data mesh, a narrower and more specific definition makes them more valuable to your organization. A well-defined scope simplifies the creation of reusable blueprints and facilitates the development of “paved paths” for building and managing data products efficiently.
Conflating data product with too many different concepts not only creates confusion among teams but also makes it significantly harder to develop reusable blueprints.
With data products, we apply many effective software engineering practices to analytical data to address common ownership and quality issues. These issues, however, aren't limited to analytical data—they exist across software engineering. There’s often a tendency to tackle all ownership and quality problems in the enterprise by riding on the coattails of data mesh and data products. While the intentions are good, we've found that this approach can undermine broader data mesh transformation efforts by diluting the language and focus.
One of the most prevalent misunderstandings is conflating data products with data-driven applications. Data products are natively designed for programmatic access and composability, whereas data-driven applications are primarily intended for human interaction and are not inherently composable.
Here are some common misrepresentations that I’ve observed and the reasoning behind it :
| Name | Reasons | Missing Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Data warehouse | Too large to be an independent composable unit. |
|
| PDF report | Not meant for programmatic access. |
|
| Dashboard | Not meant for programmatic access. While a data product can have a dashboard as one of its outputs or dashboards can be created by consuming one or more data products, a dashboard on its own do not qualify as a data product. |
|
| Table in a warehouse | Without proper metadata or documentation is not a data product. |
|
| Kafka topic | They are typically not meant for analytics. This is reflected in their storage structure — Kafka stores data as a sequence of messages in topics, unlike the column-based storage commonly used in data analytics for efficient filtering and aggregation. They can serve as sources or input ports for data products. |
|
Working backwards from a use case
Working backwards from the end goal is a core principle of software development, and we’ve found it to be highly effective in modelling data products as well. This approach forces us to focus on end users and systems, considering how they prefer to consume data products (through natively accessible output ports). It provides the data product team with a clear objective to work towards, while also introducing constraints that prevent over-design and minimise wasted time and effort.
It may seem like a minor detail, but we can’t stress this enough: there's a common tendency to start with the data sources and define data products. Without the constraints of a tangible use case, you won’t know when your design is good enough to move forward with implementation, which often leads to analysis paralysis and lots of wasted effort.
How to do it?
The setup
This process is typically conducted through a series of short workshops. Participants should include potential users of the data product, domain experts, and the team responsible for building and maintaining it. A white-boarding tool and a dedicated facilitator are essential to ensure a smooth workflow.
The process
Let's take a common use case we find in fashion retail.
Use case:
As a customer relationship manager, I need timely reports that provide insights into our most valuable and least valuable customers. This will help me take action to retain high-value customers and improve the experience of low-value customers.
To address this use case, let's define a data product called “Customer Lifetime Value” (CLV). This product will assign each registered customer a score that represents their value to the business, along with recommendations for the next best action that a customer relationship manager can take based on the predicted score.
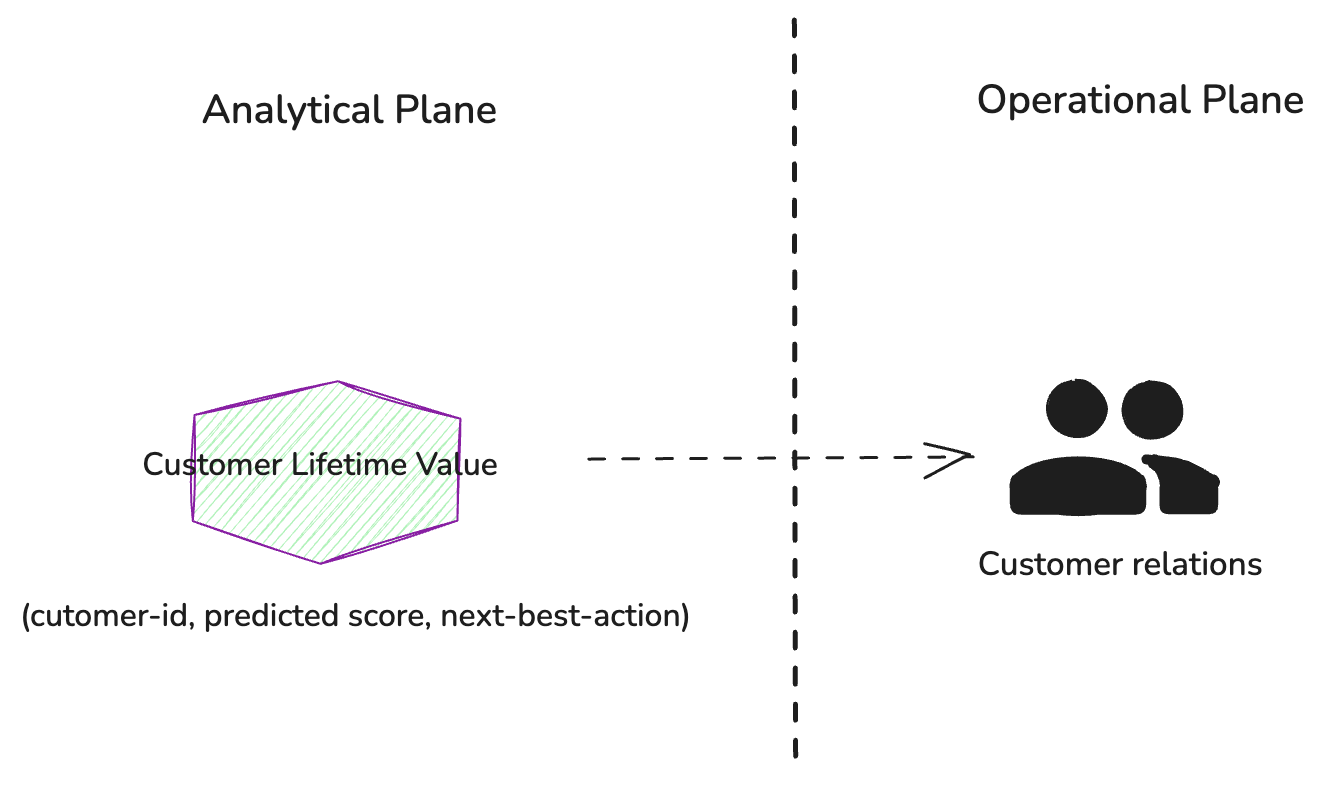
Figure 1: The Customer Relations team uses the Customer Lifetime Value data product through a weekly report to guide their engagement strategies with high-value customers.
Working backwards from CLV, we should consider what additional data products are needed to calculate it. These would include a basic customer profile (name, age, email, etc.) and their purchase history.
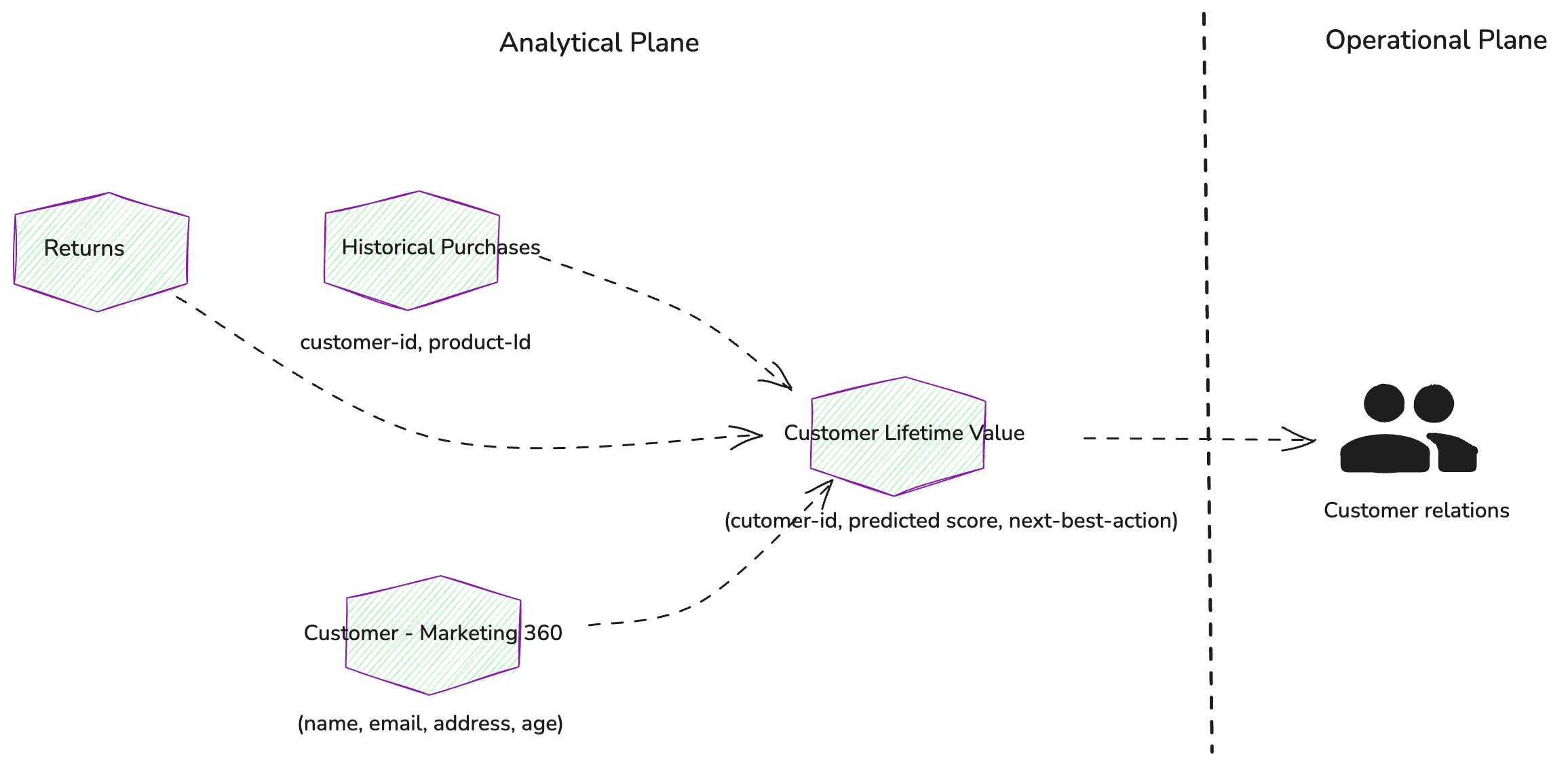
Figure 2: Additional source data products are required to calculate Customer Lifetime Values
If you find it difficult to describe a data product in one or two simple sentences, it’s likely not well-defined
The key question we need to ask, where domain expertise is crucial, is whether each proposed data product represents a cohesive information concept. Are they valuable on their own? A useful test is to define a job description for each data product. If you find it difficult to do so concisely in one or two simple sentences, or if the description becomes too long, it’s likely not a well-defined data product.
Let’s apply this test to above data products
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) :
Delivers a predicted customer lifetime value as a score along with a suggested next best action for customer representatives.
Customer-marketing 360 :
Offers a comprehensive view of the customer from a marketing perspective.
Historical Purchases:
Provides a list of historical purchases (SKUs) for each customer.
Returns :
List of customer-initiated returns.
By working backwards from the “Customer - Marketing 360”, “Historical Purchases”, and “Returns” data products, we should identify the system of records for this data. This will lead us to the relevant transactional systems that we need to integrate with in order to ingest the necessary data.
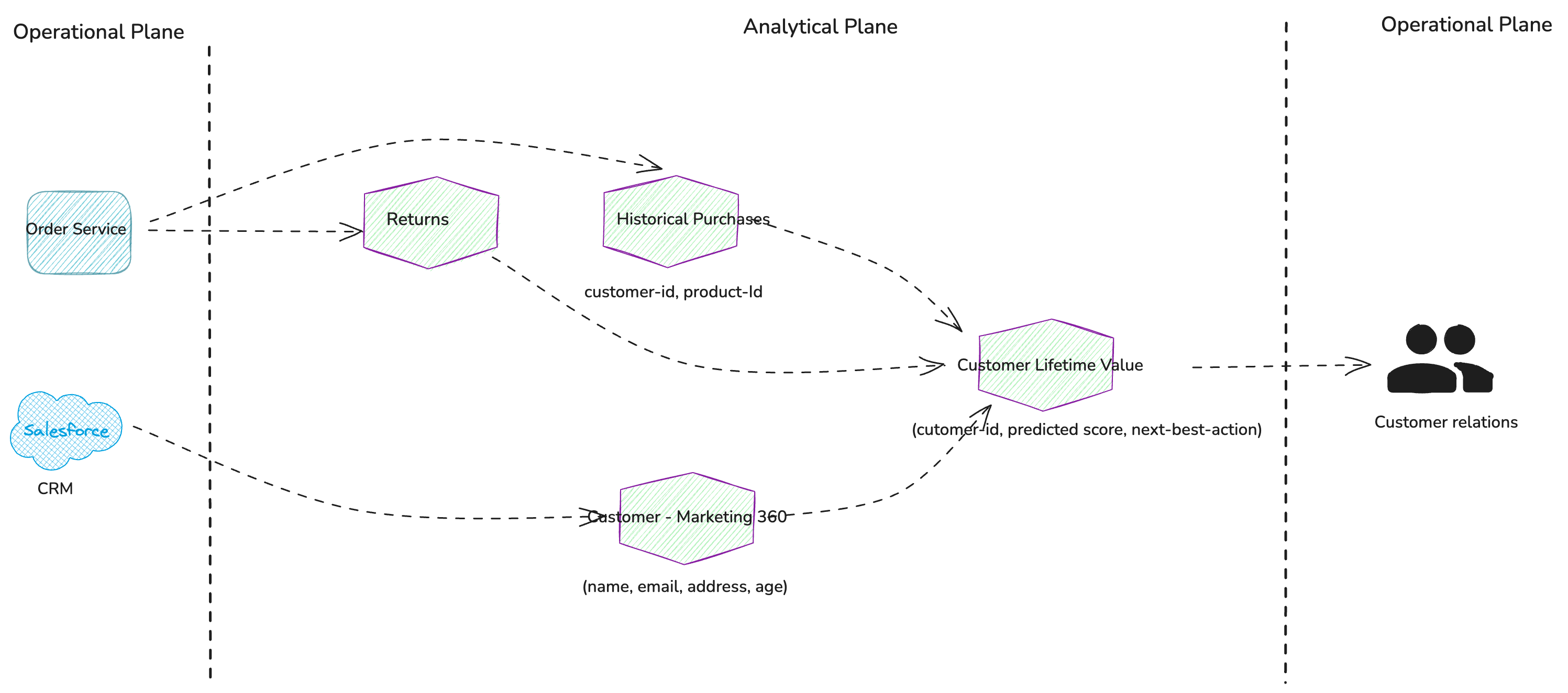
Figure 3: System of records or transactional systems that expose source data products
Overlay additional use cases and generalise
Now, let's explore another use case that can be addressed using the same data products. We'll apply the same method of working backwards, but this time we'll first attempt to generalise the existing data products to fit the new use case. If that approach isn't sufficient, we'll then consider developing new data products. This way we’ll ensure that we are not overfitting our data products just one specific use case and they are mostly reusable.
Use case:
As the marketing backend team, we need to identify high-probability recommendations for upselling or cross-selling to our customers. This will enable us to drive increased revenue..
To address this use case, let's create a data product called “Product Recommendations” which will generate a list of suggested products for each customer based on their purchase history.
While we can reuse most of the existing data products, we’ll need to introduce a new data product called “Products” containing details about all the items we sell. Additionally, we need to expand the “Customer-Marketing 360” data product to include gender information.
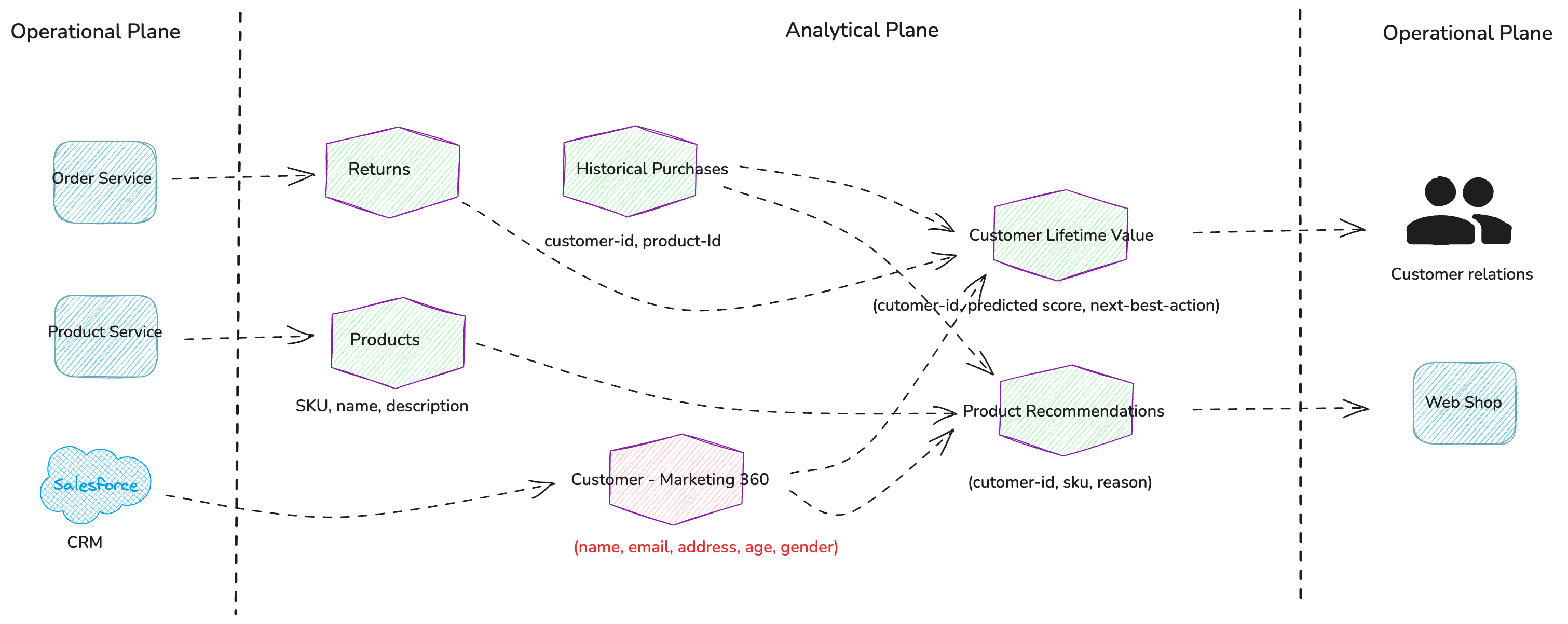
Figure 4: Overlaying Product Recommendations use case while generalizing existing data products
So far, we’ve been incrementally building a portfolio (interaction map) of data products to address two use cases. We recommend continuing this exercise up to five use cases; beyond that, the marginal value decreases, as most of the essential data products within a given domain should be mapped out by then.
Assigning domain ownership
After identifying the data products, the next step is to determine the Bounded Context or domains they logically belong to.
No single data product should be owned by multiple domains, as this can lead to confusion and finger-pointing over quality issues.
This is done by consulting domain experts and discussing each data product in detail. Key factors include who owns the source systems that contribute to the data product, which domain has the greatest need for it, and who is best positioned to build and manage it. In most cases, if the data product is well defined and cohesive, i.e. “valuable on its own”, the ownership will be clear. When there are multiple contenders, it's more important to assign a single owner and move forward—usually, this should be the domain with the most pressing need. A key principle is that no single data product should be owned by multiple domains, as this can lead to confusion and finger-pointing over quality issues.
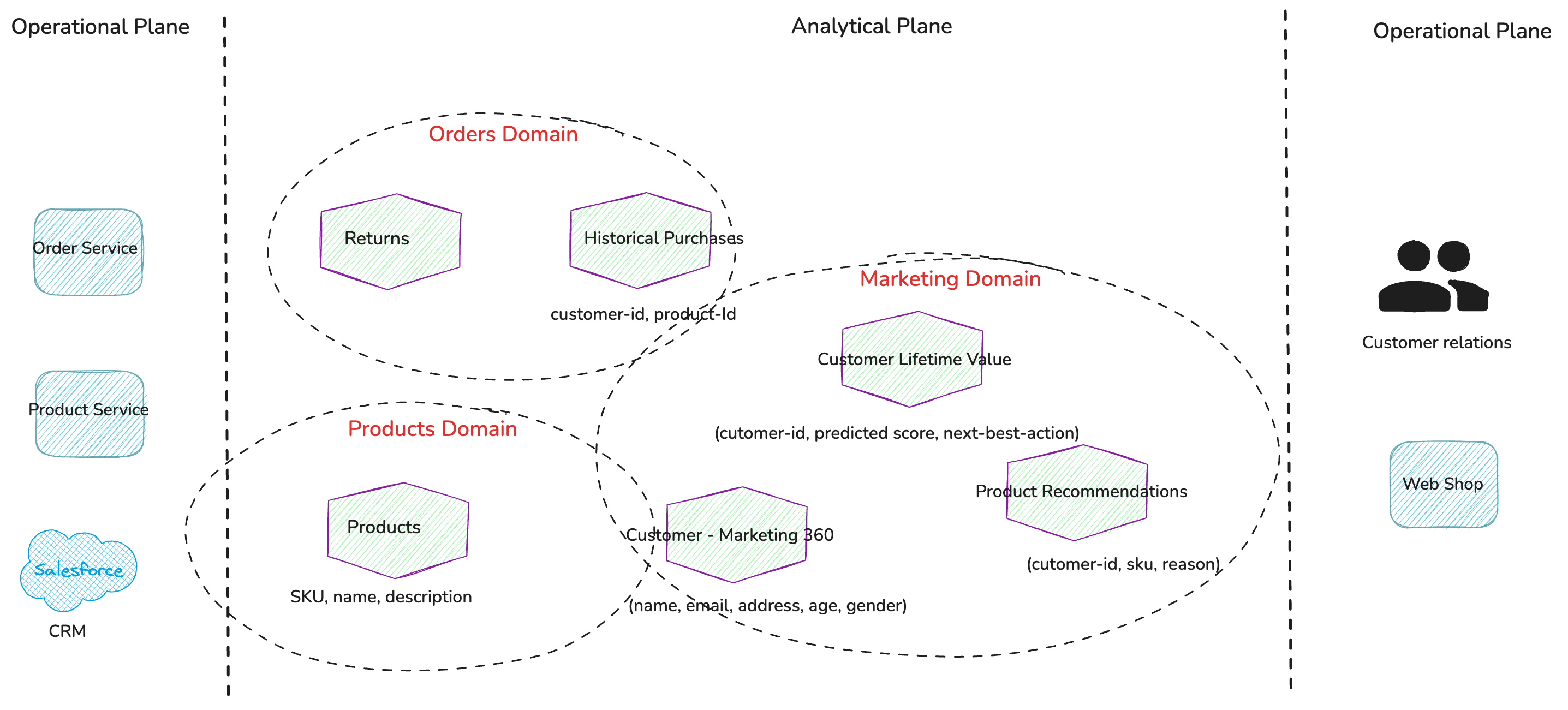
Figure 5: Mapping data products to their respective domains.
The process of identifying the set of domains in your organization is beyond the scope of this article. For that, I recommend referring to Eric Evans' canonical book on Domain-Driven Design and the Event Storming technique.
While it's important to consider domain ownership early, it’s often more efficient to have a single team develop all the necessary data products to realise the use case at the start of your data mesh journey. Splitting the work among multiple teams too early can increase coordination overhead, which is best delayed. Our recommendation is to begin with a small, cohesive team that handles all data products for the use case. As you progress, use “team cognitive load” as a guide for when to split into specific domain teams.
Having a consistent blueprints for all data products will make this transition of ownership easier when the time comes. The new team can focus solely on the business logic encapsulated within the data products, while the organization-wide knowledge of how data products are built and operated is carried forward.
Defining service level objectives (SLOs)
SLOs will guide the architecture, solution design and implementation of the data product
The next step is to define service level objectives (SLOs) for the identified data products. This process involves asking several key questions, outlined below. It is crucial to perform this exercise, particularly for consumer-oriented data products, as the desired SLOs for source-oriented products can often be inferred from these. The defined SLOs will guide the architecture, solution design and implementation of the data product, such as whether to implement a batch or real-time processing pipeline, and will also shape the initial platform capabilities needed to support it
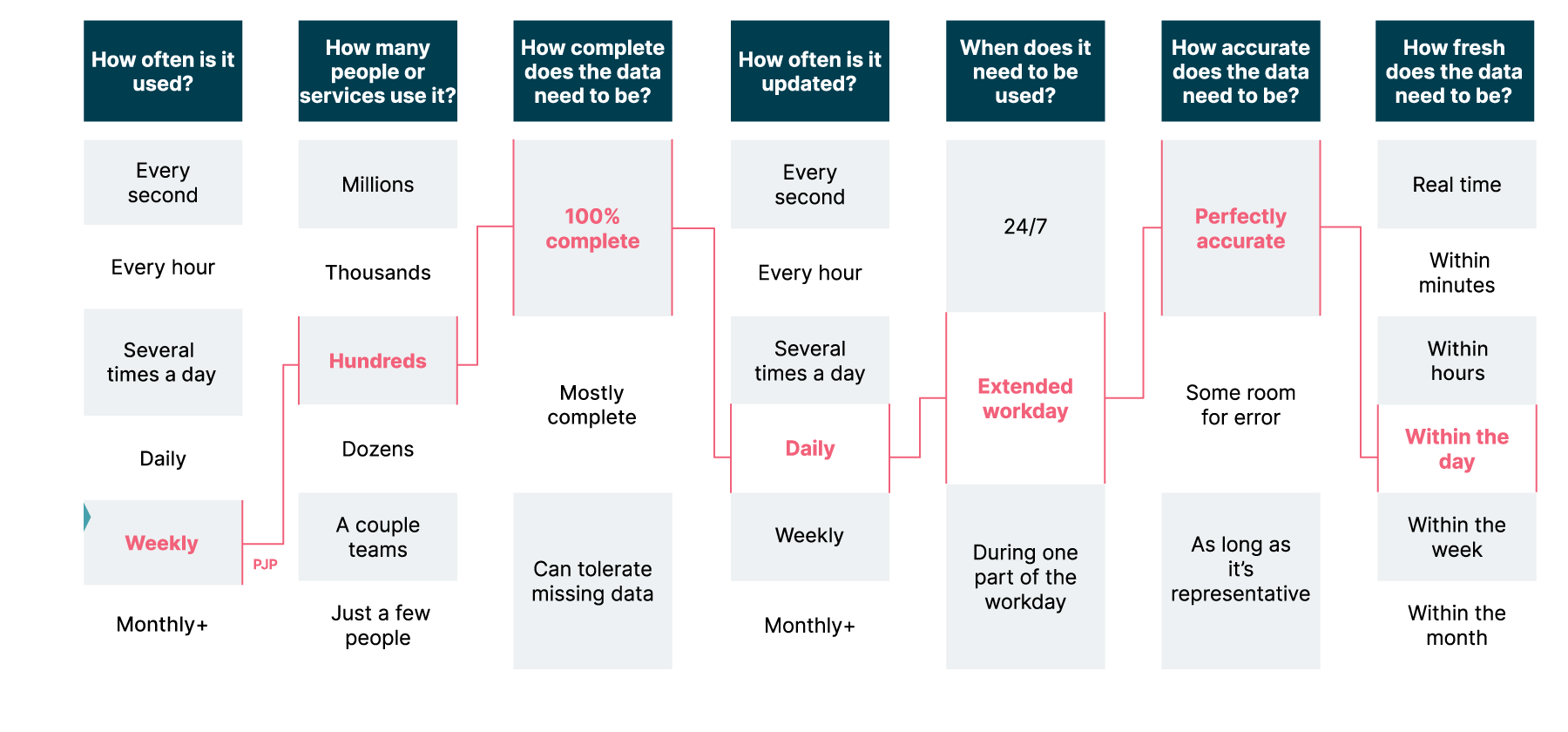
Figure 6: Guiding questions to help define Service level objectives for data products
During implementation, measurable Service Level Indicators (SLIs) are derived from the defined SLOs, and platform capabilities are utilized to automatically measure and publish the results to a central dashboard or a catalog. This approach enhances transparency for data product consumers and helps build trust. Here are some excellent resources on how to achieve this: A step-by-step guide and Building An “Amazon.com” For Your Data Products.
How big should data products be?
For structured data, this usually means a single denormalized table, and for semi-structured or unstructured data, a single dataset. Anything larger is likely trying to do too much
This is a common question during the design phase and will sound familiar to those with experience in microservices. A data product should be just large enough to represent a cohesive information concept within its domain. For structured data, this usually means a single denormalized table, and for semi-structured or unstructured data, a single dataset. Anything larger is likely trying to do too much, making it harder to explain its purpose in a clear, concise sentence and reducing its composability and reusability.
While additional tables or interim datasets may exist within a data product’s pipeline, these are implementation details, similar to private methods in a class. What truly matters is the dataset or table the data product exposes for broader consumption, where aspects like SLOs, backward compatibility, and data quality come into play
We’ve designed data products - what next?
So far, we’ve established the logical boundaries of data products, defined their purpose, set their service level objectives (SLOs) and identified the domains they’d belong to. This foundation sets us up well for implementation.
Although a complete implementation approach could warrant its own article (Implementing Data Products), I’ll highlight some key points to consider that build directly on the design work we've done so far.
Identify patterns and establish paved roads
Identify common patterns and create reusable blueprints for data products.
When designing data products, we focus on making them simple and cohesive, with each data product dedicated to a single, well-defined function. This simplicity allows us to identify common patterns and develop reusable blueprints for data products.
We focus on identifying shared patterns across input, output, transformation, data quality measurement, service levels, and access control that our defined set of dat products must adhere to.
Here’s what it might look like for the above-identified set of data products:
| Pattern | Options |
|---|---|
| Input | FTP, S3 bucket, API , Other data products |
| Output | APIs, Table, S3 bucket, ML model with an inference endpoint |
| Transformation | SQL transformations, Spark jobs |
| Service Levels | SLIs specified by data product team; centrally measured and published by the platform |
| Access control | Rules specified by data product team; enforced by the platform |
Provide a seamless developer experience
Once the common shared patterns are identified, it is the platform's responsibility to provide a “paved road” — an easy, compliant and self-service way to build and operate data products.
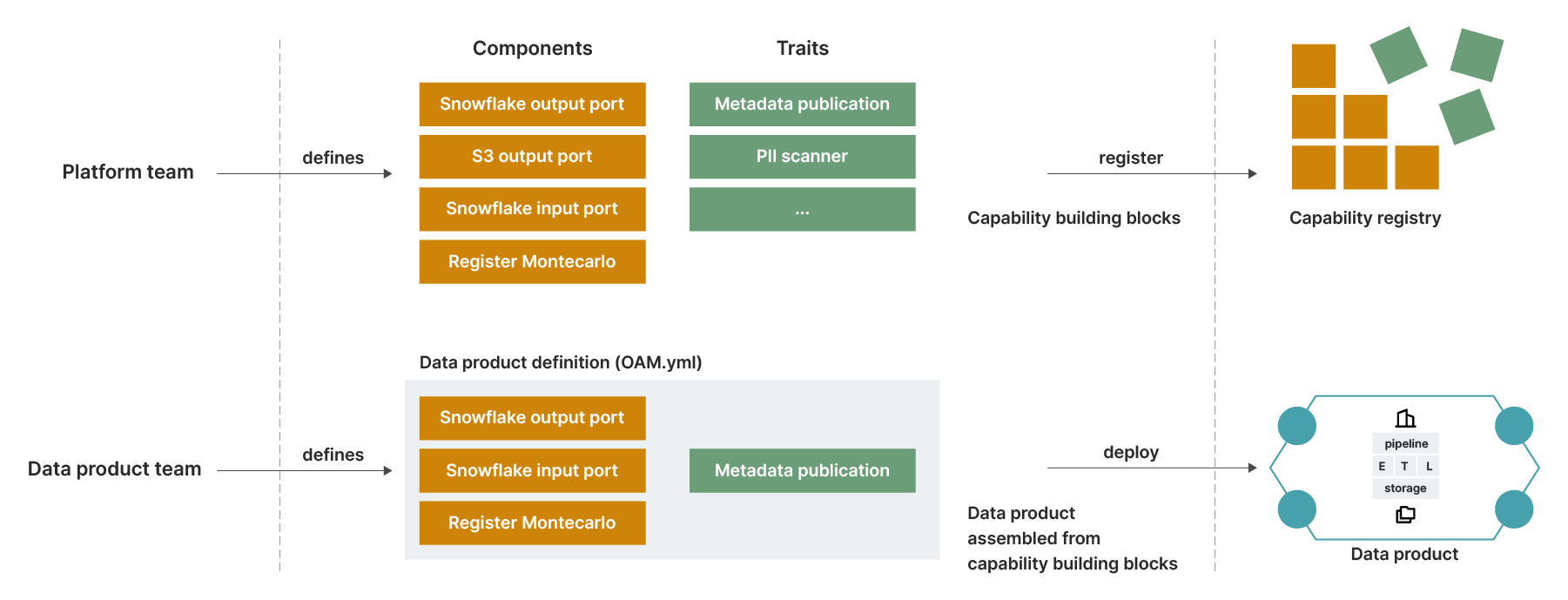
Figure 7: Clear separation of responsibilities between the platform team and the data product team.
In our implementations, this has been achieved through a specification-driven developer experience. The platform offers blueprints and capabilities that data product developers can leverage using declarative specifications, enabling them to assemble data products based on predefined blueprints and patterns.
This approach allows developers to focus on delivering business value while the platform abstracts away common engineering concerns shared across all data products.
Setup independent source control and deployment pipelines
In our experience, it's beneficial for each data product identified earlier to have its own source control repository and associated deployment pipeline, allowing for independent management of its lifecycle. This repository would ideally contain all the essential structural elements needed to build and operate the data product, including:
In our experience, it's beneficial for each data product to have its own source control repository and associated deployment pipeline
- Code or specifications to provision necessary infrastructure, such as storage and compute resources.
- Code for data ingestion, transformation, and output processes.
- Access policies and rules, defined as code or specifications.
- Code for measuring and reporting data quality metrics and service level indicators.
Automate governance
In a data mesh, data products are typically built and owned by different independent teams. We rely on automation to ensure data products are built following best practices and align with organization-wide standards, enabling seamless interoperability.
Fitness functions are an excellent technique for automating governance rules. They can be implemented and executed centrally in the platform, with dashboards used to publish the results of these automated checks. This, in turn, encourages teams to play by the rules.
Conclusion
Since data mesh came to the fore half a decade ago, we've seen many organisations embrace its vision but struggle to operationalise it effectively. This series of articles on data products aims to provide practical, experience-based guidance to help organisations get started. I often advise my clients that if they need to prioritise one aspect of data mesh, it should be “data as a product”. Focusing on getting that right establishes a strong foundation, enabling the other pillars to follow naturally. Hopefully, the techniques outlined in this article will help you design better data products and set you up for success in your data mesh journey.
Let us know how it goes!
Acknowledgements
Thanks to Martin Fowler for encouraging me to write this. Zhamak Dehghani, for the one-line brief years ago — “work backwards from the use case” — when we were all figuring out what data mesh is and how to implement it. Ecem Biyik, Ammara Gafoor and Maite Gorostiaga for running countless data product discovery workshops with me. My amazing tech leads Manisha Jain, Pablo Porto and Darren Young, who took these ideas and ran with them. Lauris Jullien, for reviewing the early draft, and Chris Ford, Arif Wider, David Lucas, Ahmet Sakar, and Chad Wathington, for their detailed reading and feedback.
Footnotes
1: we refer to such a unit as an architectural quantum
Significant Revisions
10 December 2024: Published remainder of the article
04 December 2024: Published up to defining service level objectives
03 December 2024: published up to working backwards from a use case

